Embark on a journey through the realm of interior architecture, where creativity meets functionality to shape captivating spaces that inspire and delight. This introduction sets the stage for a deep dive into the intricate world of design, blending innovation with tradition to create harmonious environments that leave a lasting impression.
In the subsequent paragraphs, readers will uncover the essence of interior architecture, from its key elements to the principles that govern its creation, all while exploring the impact of technology and cultural influences on this dynamic field.
Overview of Interior Architecture
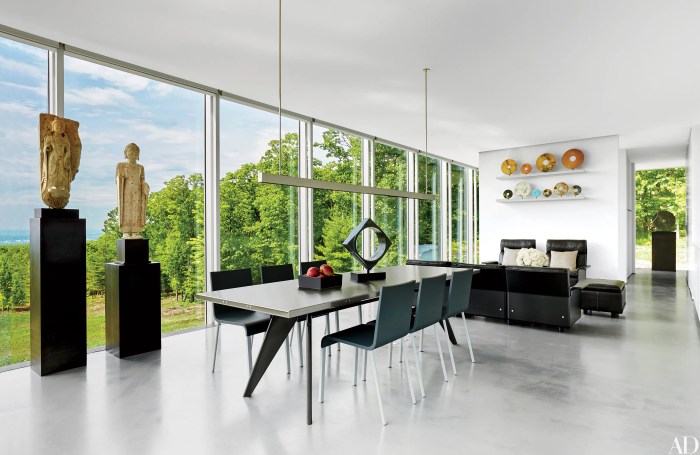

Interior architecture focuses on the design and optimization of interior spaces, considering both aesthetic and functional aspects. It involves the planning, designing, and management of interior spaces to create environments that are not only visually appealing but also practical and conducive to the activities taking place within them.Interior architecture is closely related to interior design, but while interior design focuses more on the decorative elements and aesthetics of a space, interior architecture delves deeper into the structural aspects, such as spatial planning, lighting, acoustics, and materials.
Interior architects often work closely with architects and engineers to ensure that the interior spaces complement the overall architectural design of a building.Some famous interior architecture projects include the Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao, Spain, designed by Frank Gehry, which features a striking titanium-clad exterior and innovative interior spaces that challenge traditional museum design.
Another notable project is the Sydney Opera House in Australia, designed by Jørn Utzon, with its iconic sail-like shells and intricate interior spaces that have become a symbol of modern architecture.
Elements of Interior Architecture
Interior architecture encompasses various key elements that work together to create functional and aesthetically pleasing spaces. These elements include spatial layout, materials, lighting, textures, and furniture.
Spatial Layout
The spatial layout refers to how the interior space is organized and utilized. It involves the arrangement of rooms, circulation paths, and functional zones within a space to optimize usability and flow.
Materials
The choice of materials in interior architecture plays a crucial role in defining the overall look and feel of a space. Materials such as wood, glass, metal, and stone are commonly used to add texture, color, and visual interest.
Lighting
Lighting is an essential element in interior architecture as it not only illuminates the space but also enhances the mood and ambiance. Natural light, artificial lighting fixtures, and the placement of light sources all contribute to the overall lighting design.
Textures
Textures add depth and dimension to interior spaces, creating visual and tactile interest. Textures can be introduced through materials, finishes, and furnishings to create a sense of warmth, comfort, and sophistication.
Role of Furniture
Furniture plays a significant role in interior architecture by providing functionality, comfort, and style to a space. The selection and placement of furniture pieces can influence the overall design scheme and help define the purpose of different areas within a space.
Traditional vs. Modern Approaches
In traditional interior architecture, elements like ornate decorations, intricate patterns, and rich textures are prominent. On the other hand, modern interior architecture focuses on clean lines, minimalism, and the use of innovative materials and technology to create sleek and contemporary spaces.
Principles of Interior Architecture
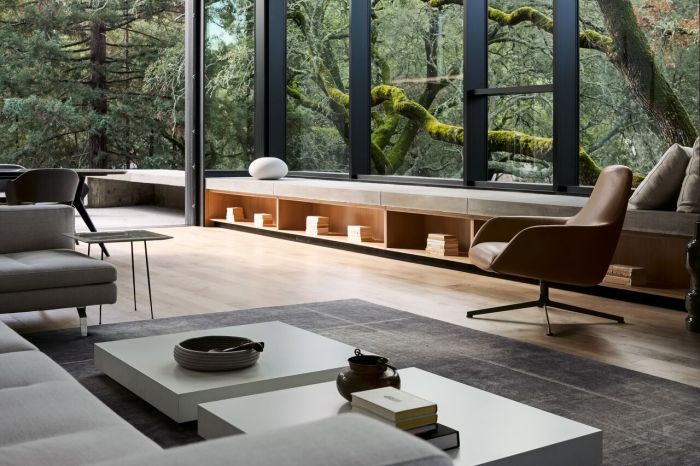

Interior architecture is guided by several key principles that help designers create functional and aesthetically pleasing spaces. These principles include balance, scale, proportion, rhythm, harmony, color theory, and sustainability.
Balance
Balance in interior architecture refers to the distribution of visual weight in a space. It can be achieved through symmetrical or asymmetrical arrangements of elements such as furniture, lighting, and accessories.
Scale and Proportion
Scale relates to the size of objects in relation to the space they occupy, while proportion deals with the relationship between these objects. Maintaining proper scale and proportion ensures that elements within a space are harmonious and well-suited to each other.
Rhythm
Rhythm in interior architecture refers to the repetition of elements to create a sense of movement and visual interest. It can be achieved through patterns, textures, or the strategic placement of objects throughout a space.
Harmony
Harmony is the overall sense of unity and cohesion in a space. It is achieved when all elements work together in a way that is visually pleasing and creates a sense of balance and tranquility.
Color Theory
Color theory plays a crucial role in interior architectural design, as different colors can evoke different emotions and set the tone for a space. Designers often use color palettes to create a cohesive and harmonious environment.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
In today's world, sustainability is a key consideration in interior architecture. Designers are increasingly incorporating eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient systems, and sustainable practices to minimize the environmental impact of their designs and create healthier living spaces.
Technology in Interior Architecture

In the field of interior architecture, technology plays a crucial role in enhancing the design process, visualizations, and overall functionality of spaces. From CAD software to virtual reality and smart home technology, advancements in technology have revolutionized how interior architecture is approached and executed.
Use of CAD Software in Design Process
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software has become an indispensable tool for interior architects. It allows designers to create detailed 2D and 3D models of spaces, enabling them to experiment with various layouts, materials, and finishes. CAD software not only streamlines the design process but also facilitates collaboration between designers, architects, and clients.
Virtual Reality in Visualizing Interior Architecture
Virtual reality has transformed the way interior architecture is visualized. Designers can now create immersive virtual environments that allow clients to experience a space before it is built. This technology provides a realistic sense of scale, proportion, and ambiance, helping clients make informed decisions and visualize the final design more accurately.
Impact of Smart Home Technology on Design
The rise of smart home technology has had a significant impact on interior architectural design. Integrating smart devices and systems into spaces has become a common practice, enhancing comfort, convenience, and energy efficiency. From automated lighting and climate control to security systems and entertainment setups, smart home technology has redefined the way spaces are designed and experienced.
Cultural Influences in Interior Architecture

Cultural influences play a significant role in shaping interior architectural styles, reflecting the values, beliefs, and traditions of different societies. Historical periods have also had a profound impact on interior architecture, with each era leaving its mark on design trends and aesthetics.
It is essential for designers to be culturally sensitive when creating interior spaces to ensure that they resonate with the intended users.
Diversity in Interior Architectural Styles
Interior architectural styles vary greatly across different cultures, showcasing unique design elements and materials that reflect the local traditions and customs. For example, Japanese interior architecture is known for its minimalistic approach, utilizing natural materials like wood and paper screens to create serene and harmonious spaces.
In contrast, Middle Eastern interior architecture often features intricate patterns, vibrant colors, and luxurious fabrics inspired by the region's rich history and heritage.
Historical Influences on Interior Architecture
Historical periods such as the Renaissance, Baroque, and Art Deco have significantly influenced interior architecture through their distinct design principles and aesthetics. For instance, the Renaissance period in Europe brought about a revival of classical elements, leading to the use of symmetry, proportion, and ornate decorations in interior spaces.
Similarly, the Art Deco movement of the 1920s and 1930s introduced geometric shapes, bold colors, and luxurious materials into interior design, reflecting the modernist ideals of the time.
The Significance of Cultural Sensitivity
Cultural sensitivity is crucial in designing interior spaces that respect and honor the traditions and values of different communities. By understanding the cultural context of a space, designers can create environments that feel authentic and meaningful to the users. This involves incorporating elements such as traditional motifs, materials, and colors in a thoughtful and respectful manner, ensuring that the design resonates with the cultural identity of the space.
Outcome Summary
As we conclude our exploration of interior architecture, we reflect on the rich tapestry of creativity and ingenuity that defines this discipline. From the fusion of art and science to the celebration of cultural diversity, interior architecture continues to shape our world in profound and meaningful ways.
FAQ Resource
What is the significance of balance in interior architecture?
Balance plays a crucial role in interior architecture by ensuring that visual elements are distributed harmoniously within a space, creating a sense of equilibrium and aesthetic appeal.
How does color theory influence interior architectural design?
Color theory guides interior architects in selecting hues that evoke specific emotions, create visual interest, and establish cohesive design schemes that resonate with occupants.
Why is cultural sensitivity important in designing interior spaces?
Cultural sensitivity is vital in interior architecture to respect and honor diverse traditions, aesthetics, and values, fostering inclusive environments that reflect the richness of human experiences.